Running a business in Canada comes with various responsibilities, including managing payroll deductions and remittances. Remitting is the process of paying tax, Pension Plan contributions (CPP/QPP) and Employment Insurance (EI) to the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) or Revenu Quebec (RQ). Understanding and properly handling these financial obligations is essential to ensure compliance with Canadian tax laws and provide your employees with accurate paychecks. In this article, we will break down the basics of payroll deductions and remittances in Canada.
In this blog we’ll cover:
- Payroll source deductions including tax, CPP/QPP and EI
- Payroll remittance
- Tools for understanding payroll deductions
What are Payroll Source Deductions?
Payroll deductions refer to the amounts that employers withhold from their employees' paychecks to meet various statutory requirements. These deductions typically fall into three main categories:
Income Tax
Employers are responsible for withholding federal and provincial income tax from their employees' earnings. The exact amount to be deducted depends on the employee's taxable income and the province in which they work.
TD1 forms should be completed by each employee at the beginning of each calendar year, or when they are first hired to indicate their personal tax credit entitlements, such as the basic personal amount and other credits for which they may be eligible. These forms are critical because they enable employers to calculate the precise amount of tax to withhold from each employee’s pay. Employers are required to keep a completed TD1 form on file for every employee and update the records whenever there is a change in an employee’s tax situation, such as a change in personal credits, marital status, or number of dependents.
Employers must ensure that their calculations reflect the latest legislative requirements and that any tax credits or exemptions claimed on the TD1 forms are applied accurately. This helps avoid both under- and over-deduction of income tax, supporting compliance and maintaining accurate payroll records.
For federal income tax, standardized rates are provided annually by the Canada Revenue Agency. Provincial and territorial income tax rates can vary, so it is essential to refer directly to the CRA website for current details. Visit the CRA website for provincial income tax rates or download The Ultimate Canadian Payroll Guide here for more information.
Canada Pension Plan (CPP) or Québec Pension Plan (QPP) Contributions
Both employees and employers are required to contribute to the CPP, which provides a retirement pension and other benefits. If you are self-employed you must also contribute. The CPP contribution rate is set by the government and is based on the employee's income, up to a maximum yearly limit.
CPP contributions are only mandatory for workers 18 years or age and older. Beginning January 1, 2024, you must deduct the second additional CPP contributions (CPP2) on earnings above the annual maximum pensionable earnings. Read more about the 2024 changes to CPP contributions here.
For Quebec-based employees, the Québec Pension Plan (QPP) operates in parallel to the CPP but is administered by Revenu Québec instead of the federal government. Both employees and employers in Quebec must contribute to the QPP, which also covers retirement, survivor, and disability benefits.
The QPP contribution rates, annual maximums, and rules are set by the province and may differ from those established under the CPP. Self-employed Quebec workers contribute both portions of QPP, similar to the CPP structure. Notably, the QPP has also implemented enhancements, and as of January 1, 2024, a second additional contribution applies to pensionable earnings above the annual maximum, mirroring the changes seen with CPP2.
Employers and payroll administrators must carefully track whether employees are covered under CPP or QPP based on their province of employment, as contribution rates, maximum amounts, and remittance procedures differ. Up-to-date information on QPP rates and requirements can be found on the Revenu Québec website.
Employment Insurance (EI) Premiums
Employees and employers must also contribute to the Employment Insurance (EI) program, which provides temporary financial assistance to individuals who are unemployed or unable to work due to specific circumstances such as job loss, illness, or parental leave. For most provinces and territories, EI premiums are calculated based on the employee’s insurable earnings at a rate set annually by the federal government.
For employees working in Quebec, the province administers its own parental insurance plan—the Québec Parental Insurance Plan (QPIP)—which covers maternity, paternity, parental, and adoption benefits.
As a result, Quebec employees and employers pay a reduced federal EI premium rate, while also contributing separately to QPIP as required by provincial legislation. The distinct rates for Quebec are set to reflect the coordination between EI and QPIP, ensuring appropriate coverage for all relevant benefits.
Employers should verify whether their employees are subject to the standard EI rate or the Quebec-specific rate, as this impacts both payroll calculations and remittances.
Additional deductions may include union dues, pension plan contributions, and other voluntary deductions as per employment agreements.
Understanding Payroll Remittances
The remittance process in Canada involves withholding payroll deductions from employees' paychecks and submitting these funds to the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) on a regular basis, either monthly or quarterly, depending on your business's average monthly withholding amount.
t's crucial to meet CRA's deadlines, use approved payment methods, and maintain accurate records to avoid penalties and interest charges. Before you remit you will need all of the following information:

Several key considerations when remitting payroll deductions to the CRA include:
- Reporting Frequency: Your reporting frequency for remitting source deductions to the CRA depends on your average monthly withholding amount. If your average monthly withholding is $1,000 or less, you can remit quarterly. If it's more than $1,000, you must remit monthly. If you are a new employer (whose payroll account has been open for less than 12 months), you can remit quarterly unless the CRA tells you that you must remit at a different frequency. New employers must have a monthly withholding amount of less than $1,000 and maintain a perfect compliance record on all payroll and GST/HST accounts.
- Remittance Deadlines: For monthly remitters, payments are due by the 15th day of the following month. For quarterly remitters, payments are due by the 15th day of the month following the end of each calendar quarter (i.e., January 15, April 15, July 15, and October 15). When a due date falls on a Saturday, Sunday, or public holiday recognized by the CRA, your payment is considered on time if the CRA receives it on or it is processed at a Canadian financial institution on or before the next business day.
- Penalties and Interest: Failing to meet remittance deadlines may result in penalties and interest charges. Below you will find the penalties and interest charges associated with late remittance.
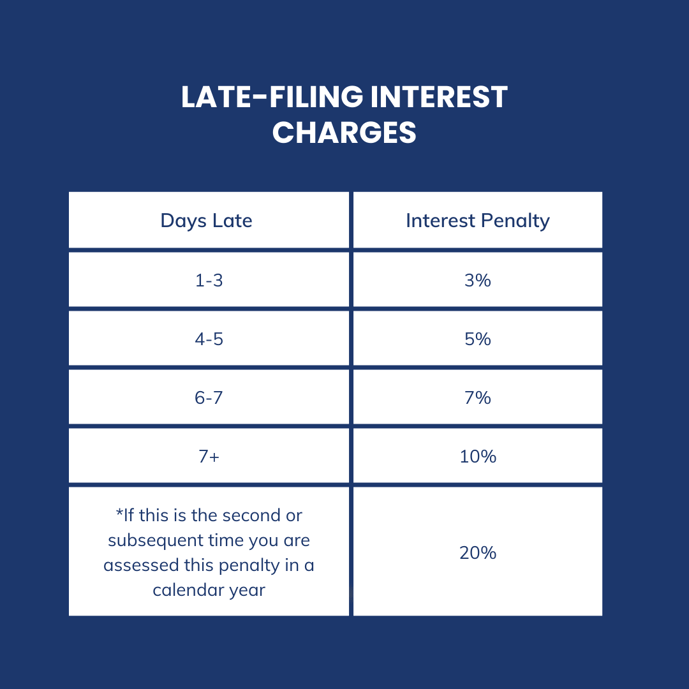
- Payment Methods: You have several options for making remittances, including online banking, financial institutions, and Canada Post. Ensure you use the correct CRA business number and account number when making payments. As of January 1st, 2024 if your remittance amounts exceed $10,000 your payments must be made electronically. Penalties may be applied unless you cannot reasonably pay the amount electronically.
- Record Keeping: It's essential to maintain accurate records of payroll deductions, remittance receipts, and related documents for at least six years. This documentation may be subject to CRA audits.
- Remitting Additional Amounts: If you have to remit additional amounts due to corrections or adjustments, you should do so as soon as possible to avoid interest charges.
Failing to remit these deductions on time can result in penalties and interest charges, so it's crucial to stay on top of your remittance obligations.
Payroll deductions and remittances are fundamental aspects of running a small or medium-sized business in Canada. While it may seem intricate, with the right knowledge and resources, you can navigate this process effectively. Staying up to date with changes in tax laws and regulations, or seeking assistance from payroll professionals or accounting services, can help ensure your business remains compliant and your employees are paid accurately and on time.
Remember, payroll deductions and remittances are not only a legal obligation but also contribute to the well-being and financial security of your employees. By understanding and managing these aspects of your business efficiently, you can create a positive work environment and foster trust among your team members, ultimately contributing to the success and growth of your business in Canada.
Payroll Tools & Resources
For find more information on payroll, deductions, remittance, and compliance, visit our Resource Center. To simplify payroll deductions and remittances, consider using payroll software or outsourcing your payroll to a professional service provider.
These tools can help calculate deductions accurately and generate the necessary reports for remittance. Additionally, the CRA provides online resources, guides, and tutorials to assist businesses in managing payroll deductions and remittances.


